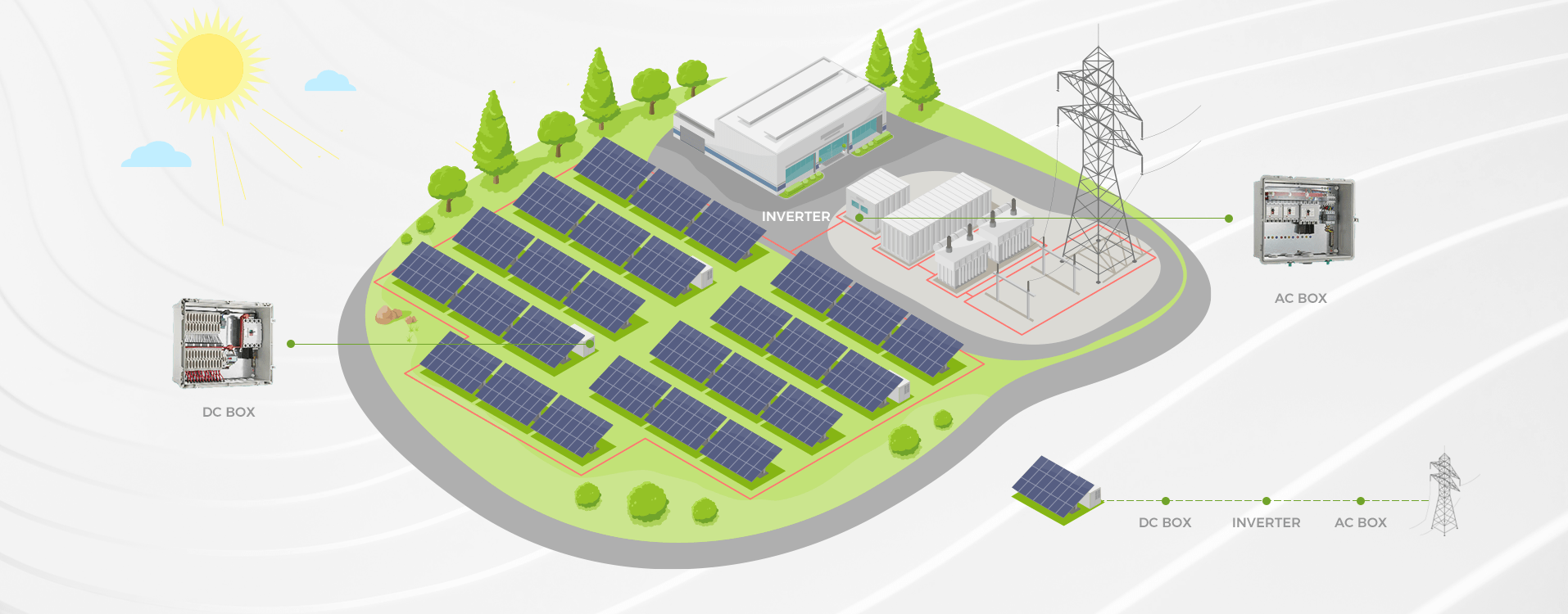
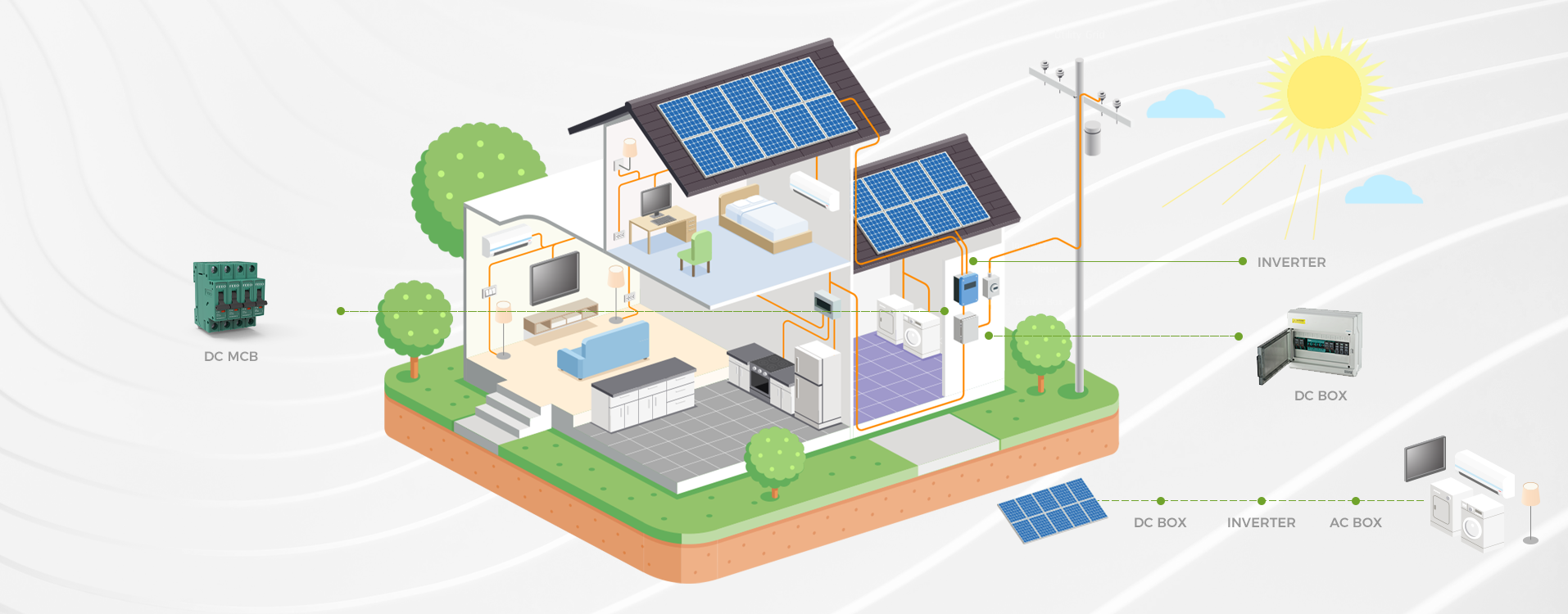
Unraveling Circuit Failures
1. Understanding Circuit Failures
Types of Failures: Circuit failures can be categorized into short circuits, open circuits, and intermittent faults. Each type presents unique challenges.
Common Causes: Overheating, component degradation, manufacturing defects, and environmental factors (like moisture or dust) often lead to failures.
2. Safety Implications
Risk Assessment: Regular assessments of circuit designs and conditions can identify potential failure points, reducing risks.
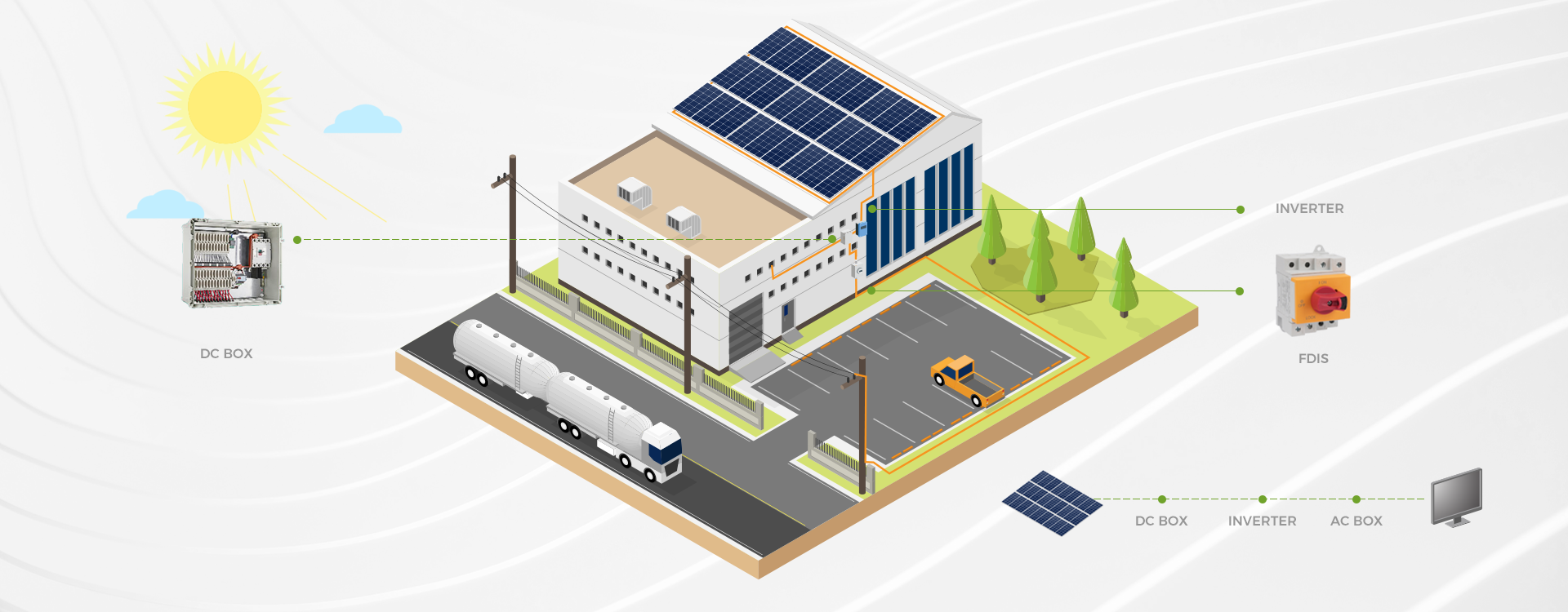
Protective Measures: Incorporating fuses, circuit breakers, and thermal protection can help mitigate hazards from failures.
3. Performance Impact
Efficiency Loss: Failures can lead to increased resistance and energy losses, affecting overall system efficiency.
Downtime and Maintenance: Frequent failures result in downtime, leading to increased operational costs and maintenance efforts.
4. Monitoring and Diagnostics
Real-Time Monitoring: Implementing sensors and diagnostic tools can provide insights into circuit health, allowing for early intervention.
Data Analysis: Analyzing failure data helps identify patterns and root causes, leading to improved designs and better performance.
5. Design Considerations
Robust Design: Designing circuits with tolerance to environmental stresses and component aging can enhance reliability.
Simulation and Testing: Utilizing simulation software during the design phase can predict how circuits will behave under various conditions.
6. Future Trends
Smart Circuits: The integration of AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance can revolutionize circuit management.
Sustainable Practices: Emphasizing sustainability in circuit design can reduce the environmental impact and improve long-term performance.
Conclusion
Addressing circuit failures requires a multifaceted approach that includes understanding failure types, implementing safety measures, and leveraging technology for monitoring and diagnostics. By prioritizing both safety and performance, organizations can enhance reliability and efficiency in their electrical systems.