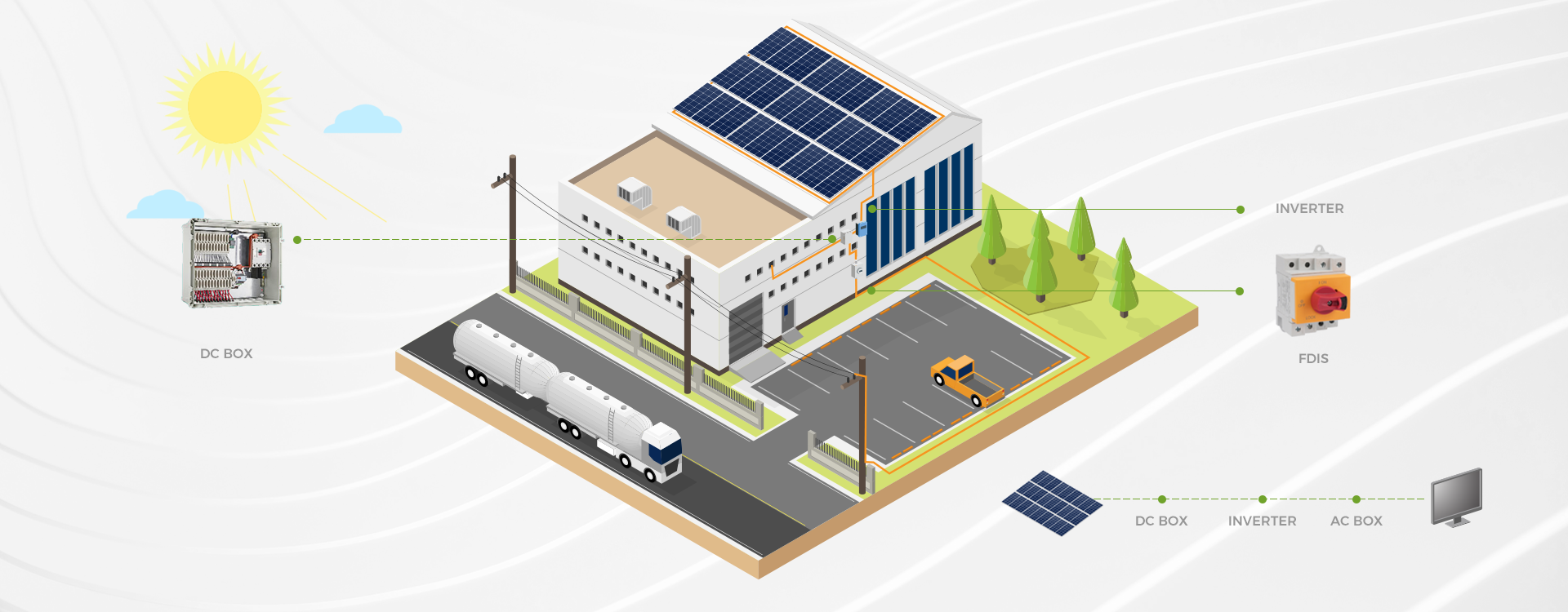
Introduction
Electricity is one of the most essential things in our daily lives, but it can also be dangerous if not handled properly. To prevent electrical hazards, there are safety devices like fuses and circuit breakers that can be used to protect electrical systems. In this article, we will discuss the difference between fuses and circuit breakers, and their functions in protecting electrical systems.
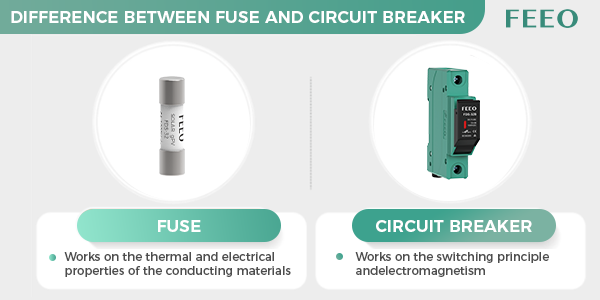
What is a Fuse?
A fuse is a safety device that protects electrical systems from overloading or short circuits. It consists of a metal wire or filament that melts when the current exceeds a certain limit, which breaks the circuit and stops the flow of electricity. Fuses are commonly used in homes, automobiles, and other electrical systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fuses
Fuses have several advantages, including low cost, simplicity, and reliable performance. They are also easy to replace and can protect against electrical fires caused by overloading or short circuits. However, fuses have some disadvantages, such as the need for regular replacement and limited protection against minor overloads. Also, once a fuse is blown, it must be replaced with a new one, which can be inconvenient.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is another safety device used to protect electrical systems. Unlike a fuse, a circuit breaker can be reset after it is tripped, and it can protect against both overloads and short circuits. A circuit breaker consists of a switch that opens and closes the circuit in response to changes in the current flow. Circuit breakers are commonly used in residential and commercial buildings, as well as in power distribution systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers have several advantages over fuses, including the ability to reset after being tripped, providing better protection against overloads and short circuits, and not needing to be replaced as often as fuses. Circuit breakers also have some disadvantages, such as higher cost and complexity, which can make them more difficult to install and maintain than fuses. Additionally, circuit breakers may not provide adequate protection against electrical fires caused by minor overloads.
Which One to Choose: Fuse or Circuit Breaker?
|
Fuse
|
Circuit Breaker
|
|
Works on the thermal and electrical properties of the conducting materials
|
Works on the switching principle and electromagnetism
|
|
It doesn’t give any indication of overloads
|
It gives an indication of overloads
|
|
Fuse can only be used once
|
A circuit breaker can be used many numbers of times
|
|
Provides protection against power overloads
|
Provides protection against power overloads and short circuits
|
|
It detects and interrupts faulty circuit conditions
|
It performs the interruption process only. Faults are detected by a relay system.
|
|
Low breaking capacity compared to the circuit breaker
|
High breaking capacity
|
|
Automatic operation
|
Can either be automatic or manually operated
|
|
Operating time of fuse is 0.002 seconds
|
Operating time of the circuit breaker is 0.02 – 0.05 seconds
|
|
Low Cost
|
High Cost
|
When it comes to choosing between fuses and circuit breakers, it depends on the specific application and the level of protection required.
For small-scale electrical systems, fuses may be more suitable due to their simplicity and low cost.
However, for larger and more complex systems, circuit breakers may be a better option because of their ability to protect against both overloads and short circuits, and the ability to reset after being tripped.
Conclusion
Fuses and circuit breakers are essential safety devices that protect electrical systems from overloading and short circuits. While fuses are simple, low cost, and reliable, they have limited protection and require regular replacement.
on the other hand, provide better protection, can be reset after being tripped, but are more complex and expensive.
Ultimately, the choice between a fuse and a circuit breaker depends on the specific application and the level of protection required. By understanding the differences between the two, you can make an informed decision and ensure the safety of your electrical system.