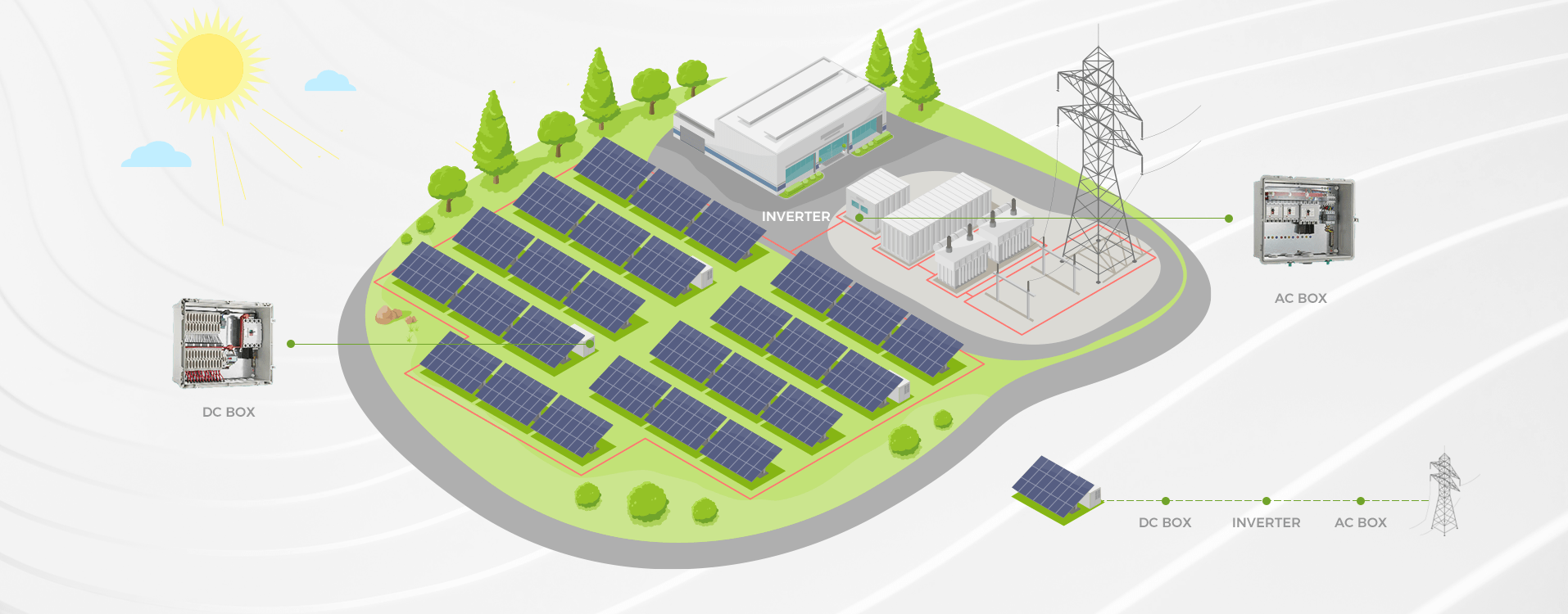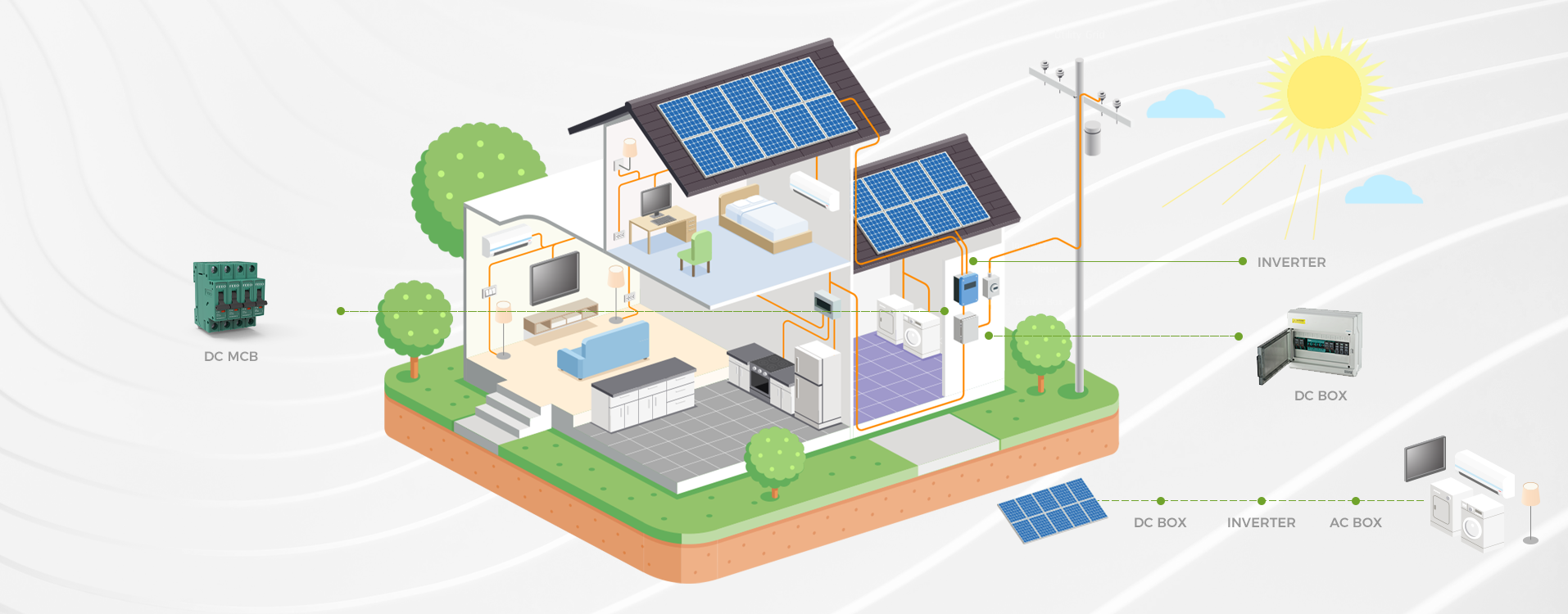
Introduction
Direct Current (DC) circuit breakers are integral components in electrical systems, designed to protect equipment and users from hazardous overcurrent situations. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the working principles, functions, and types of DC circuit breakers, as well as their crucial role in overcurrent protection.
How DC Circuit Breakers Work
A DC circuit breaker's primary function is to interrupt the flow of electrical current when it exceeds a predetermined threshold. The circuit breaker detects the overcurrent and mechanically separates the contacts, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. The primary components of a DC circuit breaker include:
-
Contacts: A set of conductive parts that allow the flow of current when closed and interrupt it when open.
-
Arc extinguishing chamber: A chamber designed to extinguish the electrical arc that forms when contacts separate.
-
Operating mechanism: The mechanism that opens and closes the contacts in response to overcurrent conditions or manual intervention.
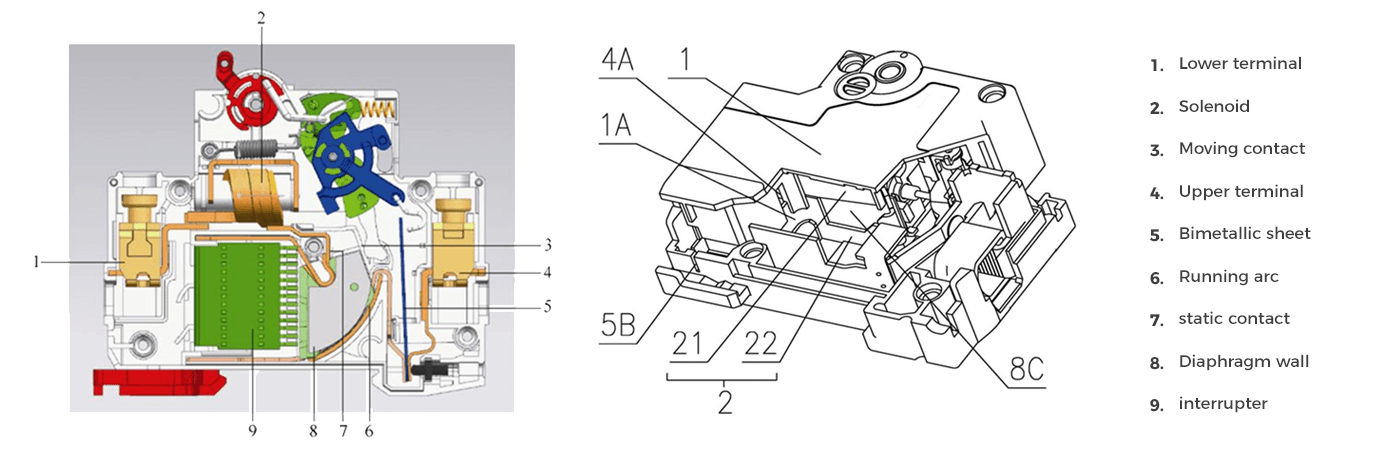
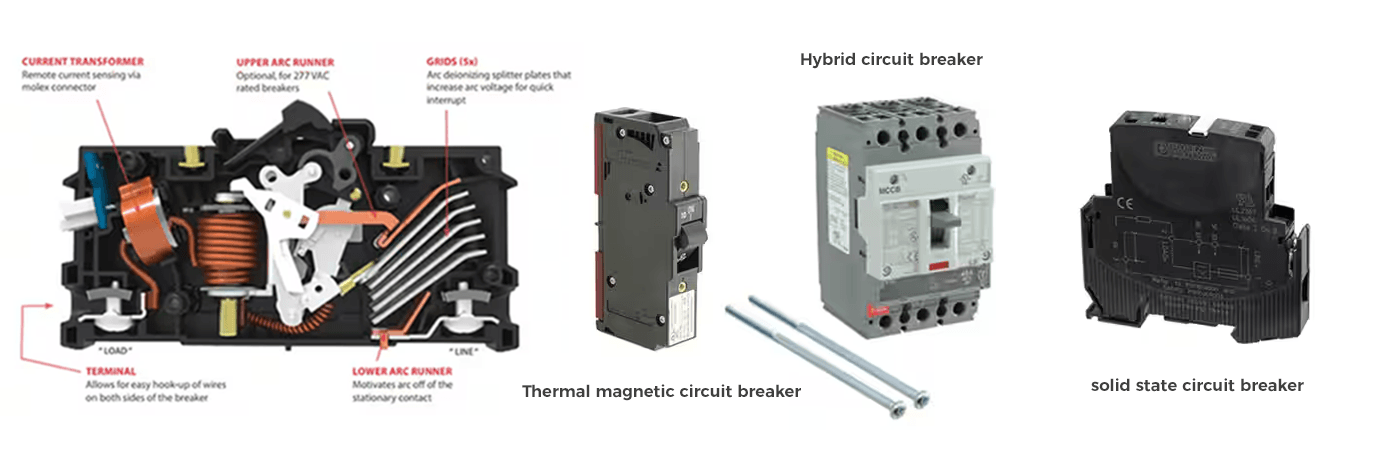
Types of DC Circuit Breakers
-
Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breakers: These breakers combine thermal and magnetic elements to respond to overcurrent situations. The thermal component reacts to slow, sustained overloads, while the magnetic component responds to short-circuit conditions.
-
Hybrid Circuit Breakers: Hybrid breakers integrate both mechanical and solid-state components, providing fast response times and reduced wear on mechanical parts. They offer advantages such as lower power consumption and the capability to handle high short-circuit currents.
-
Solid-State Circuit Breakers: These breakers use electronic components, such as transistors and microcontrollers, to detect and interrupt overcurrent conditions. Solid-state breakers offer high-speed protection and precise control, but are typically more expensive than mechanical alternatives.
DC Circuit Breaker Applications
DC circuit breakers are commonly used in various applications, including:
-
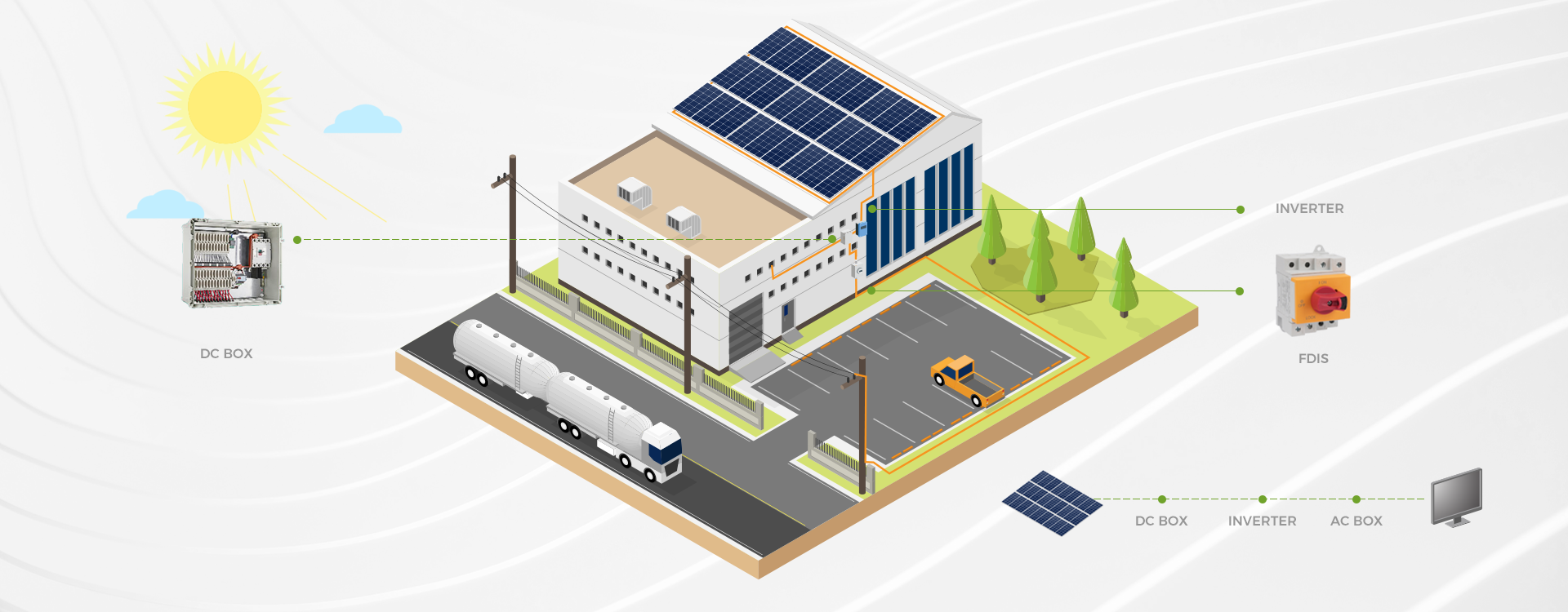
Solar power systems: Protecting solar panels and inverters from overcurrent conditions caused by faults or excessive sunlight.
-
Battery systems: Safeguarding batteries from short circuits and overloads, ensuring long life and reliable performance.
-
Electric vehicles: Protecting EV components, such as motors and charging systems, from overcurrent events.
-
Telecommunication equipment: Ensuring the safety and reliability of power supplies and communication lines in telecommunication systems.
Importance of DC Circuit Breakers in Overcurrent Protection
DC circuit breakers play a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. They provide the following benefits:
-
Equipment Protection: By interrupting overcurrent situations, circuit breakers prevent damage to electrical components, reducing the risk of equipment failure and costly repairs.
-
Personal Safety: Circuit breakers help protect individuals from electrocution and electrical fires caused by overcurrent conditions.
-
System Reliability: By limiting the impact of overcurrent events and enabling timely identification of faults, circuit breakers contribute to the overall stability and reliability of electrical systems.
-
Selective Coordination: Properly coordinated circuit breakers can isolate faults, minimizing the impact on other parts of the electrical system and allowing unaffected areas to continue operating.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine maintenance and inspection of DC circuit breakers are essential for ensuring their proper function and longevity. Some key maintenance tasks include:
-
Visual inspection: Check for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion on the breaker's contacts, arc extinguishing chamber, and operating mechanism.
-
Mechanical inspection: Verify that the operating mechanism moves freely and that the contacts open and close correctly.
-
Electrical testing: Measure the breaker's contact resistance, insulation resistance, and trip characteristics to ensure they meet the manufacturer's specifications.
In case of any issues or malfunctions, consult the manufacturer's guidelines or seek the assistance of a qualified professional to diagnose and repair the problem.
Conclusion
Understanding the principles, functions, and types of DC circuit breakers is crucial for professionals involved in electrical system design, maintenance, and operation. These devices play a vital role in overcurrent protection, safeguarding equipment, individuals, and overall system reliability. By staying informed and up-to-date on the latest advancements in circuit breaker technology, professionals can ensure the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems.