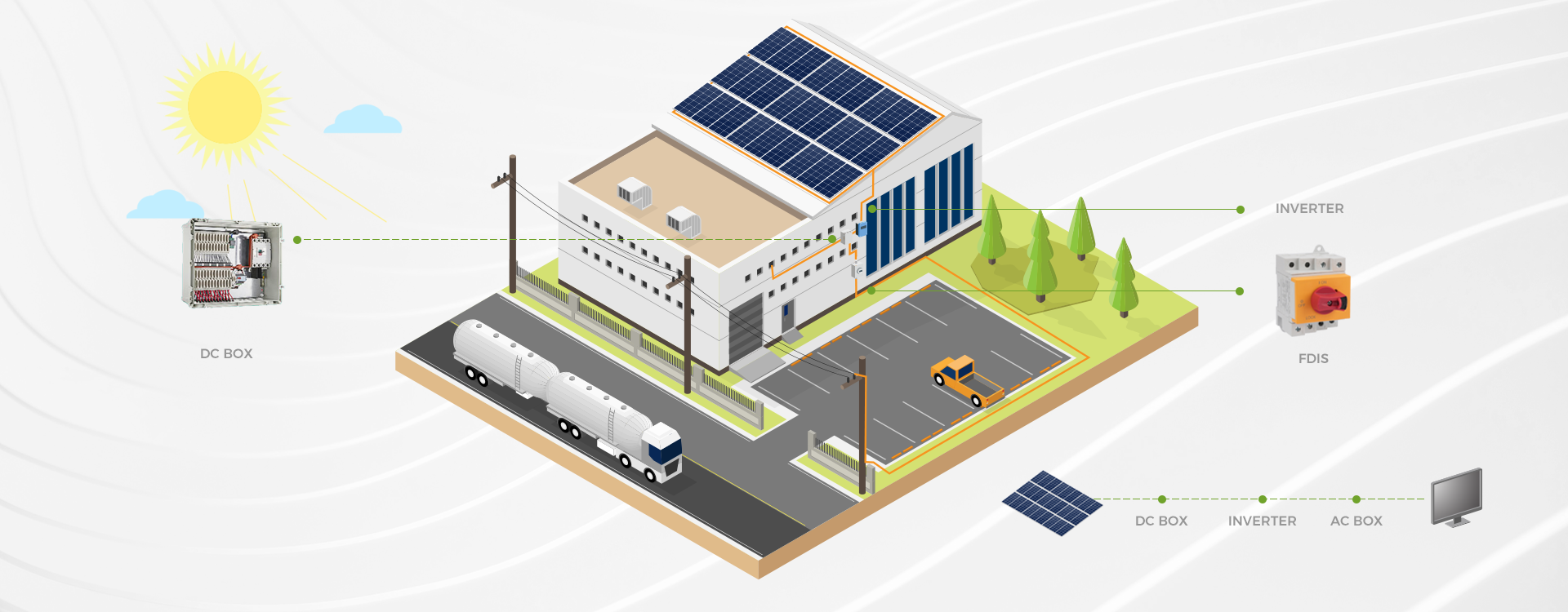
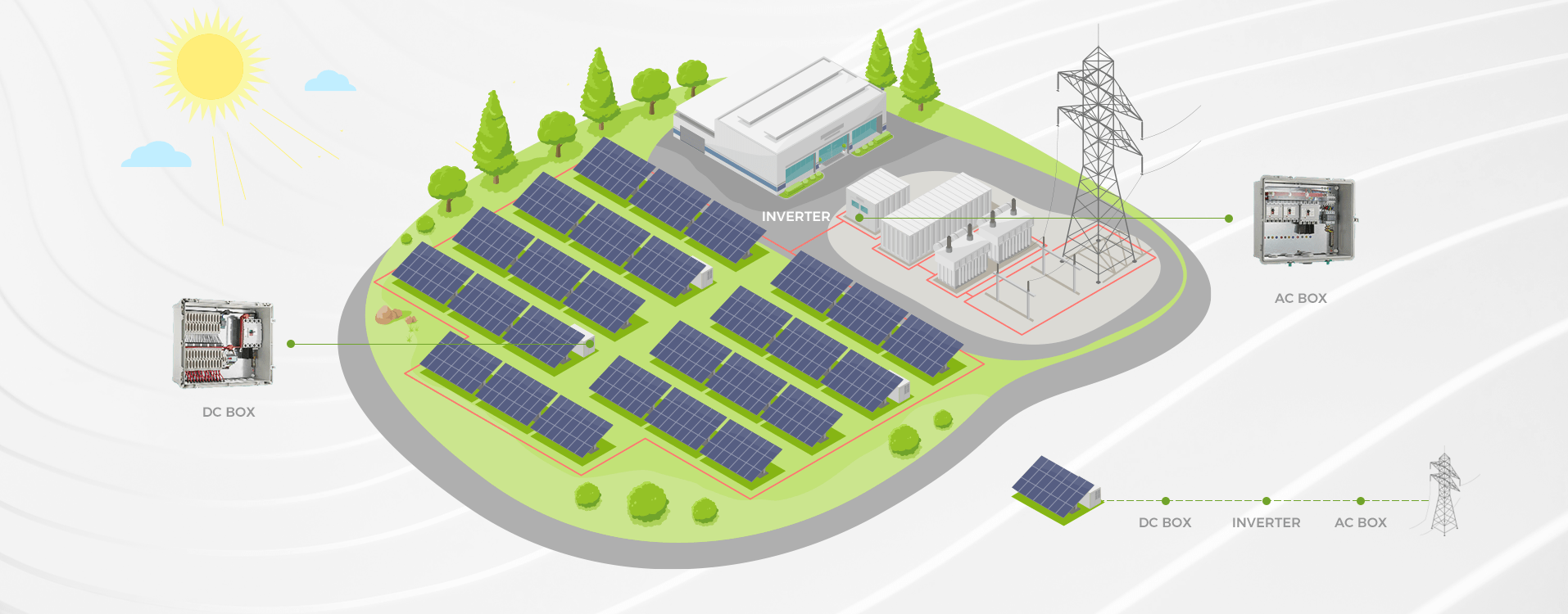
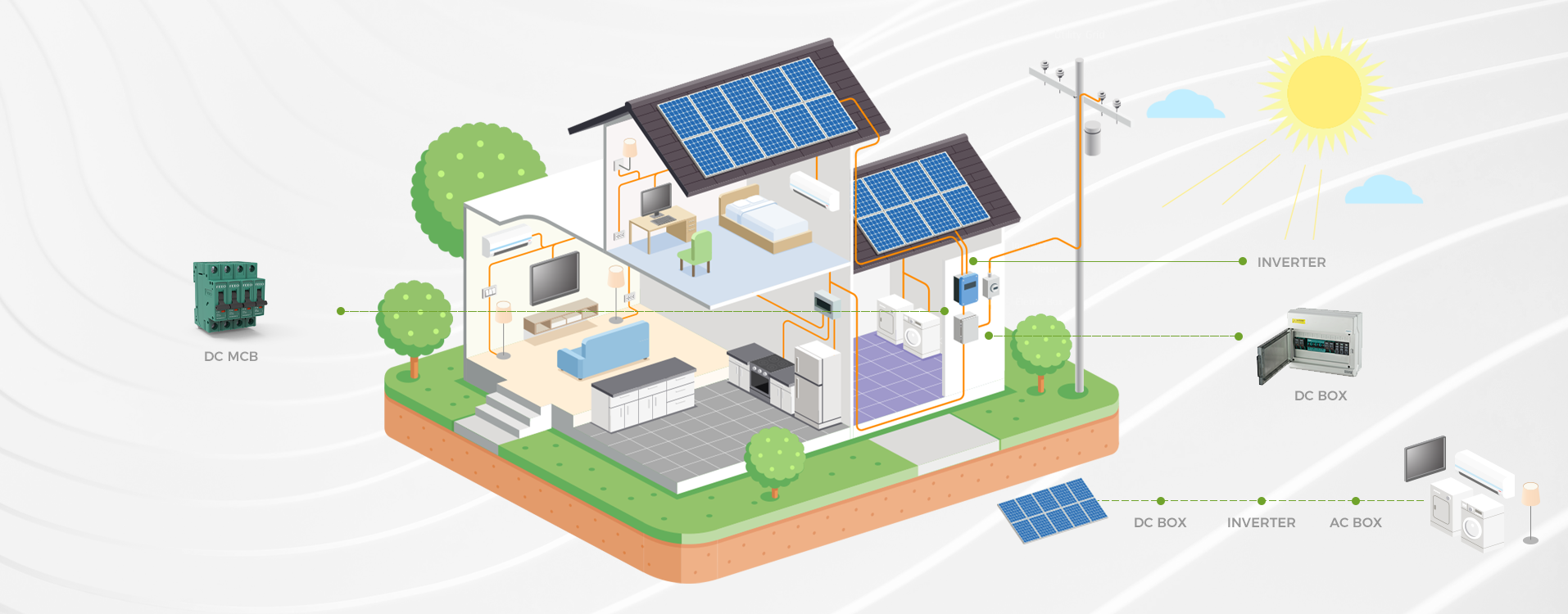
Choosing a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) for DC applications involves several important considerations. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Determine the Load Current
Calculate the total current that the circuit will draw. This is typically done based on the rated load of the connected devices.
2. Select the MCB Rating
Choose an MCB with a current rating (In) greater than the load current but not exceeding the maximum permissible rating for the wiring and devices in use. Common ratings include 1A, 2A, 4A, 6A, 10A, etc.
3. Consider the Breaking Capacity
The breaking capacity (also known as short-circuit capacity) is the maximum fault current the MCB can interrupt. Ensure this value is suitable for your application, typically expressed in kA.
4. Select the Correct Type
For DC applications, MCBs are often categorized as either Type B, C, or D based on their tripping characteristics. Type C is commonly used for motors and inductive loads, while Type B is suitable for resistive loads.
5. Voltage Rating
Ensure the MCB is rated for the specific DC voltage of your system. Common DC voltage ratings include 12V, 24V, 48V, etc.
6. Consider Environmental Factors
Check for environmental ratings (IP ratings) if the MCB will be exposed to dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures.
7. Compliance and Standards
Ensure the MCB complies with relevant standards such as IEC 60947-2 for circuit breakers.
8. Manufacturer Recommendations
Consult the manufacturer's guidelines for the specific MCB model, as different models may have unique requirements or characteristics.
9. Testing and Certification
Look for MCBs that have been tested and certified for use in DC applications to ensure safety and reliability.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can select an appropriate MCB for your DC application, ensuring safety and reliability in your electrical system.